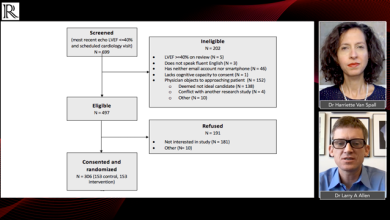
Heart failure (HF) is a rapidly growing public health issue with an estimated prevalence of >37.7 million individuals globally. HF is a shared chronic phase of cardiac functional impairment secondary to many aetiologies, and patients with HF experience a range of symptoms that affect their quality of life, including dyspnoea, fatigue, poor exercise tolerance and fluid retention.
The burden of HF will continue to rise, due to population aging, population growth and improved treatment of HF and other cardiovascular disorders. As a result, clinicians will be increasingly challenged to develop treatment plans and care systems that reduce the high levels of morbidity and mortality experienced by these patients, both from their HF and other comorbidities.